
The Power of Zinc
Share
The Power of Zinc: Unveiling Its Functions, Health Benefits, and Food Source
Are you curious about the hidden miracles that keep your body running smoothly daily? Imagine an unseen force crucial for your wellbeing, playing a significant role in everything from your immune function to your metabolism, skin health, and even your ability to taste and smell. This hero is none other than the powerful, albeit small, trace mineral known as Zinc. Today, let's unveil the mysteries and dive deep into the world of this phenomenal nutrient. Buckle up for a journey illuminating how essential Zinc is for your life and health.
Zinc, an indispensable nutrient, is crucial in various bodily functions. From skin health to immune function and cell growth, Zinc offers many benefits that can enhance your overall wellbeing. This article delves into Zinc, unravelling its functions, health advantages, recommended dosage, and possible side effects.
Understanding Zinc
You may wonder, what is Zinc? This micronutrient, though required in minute quantities, holds immense power. Its importance for our health is anything but small. Let's uncover more about this wonder mineral.
Zinc is classified as an essential nutrient, meaning your body cannot synthesize or store it naturally. Consequently, acquiring a constant zinc supply through your dietary zinc intake. This versatile mineral involves numerous physiological processes, such as gene expression, enzymatic reactions, immune function, protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, wound healing, and growth and development.

Zinc: An Essential Mineral
Now, you might still be asking yourself, what is Zinc? Let's delve a bit deeper into understanding this trace mineral. Zinc is a micronutrient that our bodies need to function optimally. Even though it falls into the 'trace' minerals category, meaning we only need a small amount, its role in maintaining our health is no longer minor.
This essential mineral is involved in numerous aspects of cellular metabolism. Over 300 enzymes in the human body require very high doses of Zinc to function correctly. These enzymes involve many physiological functions, from protein synthesis and wound healing to DNA synthesis and cell division.
Zinc also has a substantial role in the process of growth and development. It's crucial for the growth and repair of muscles and tissues, maintaining the skin's health, and supporting healthy pregnancy and childbirth.

One of the fascinating things about Zinc is that our bodies don't store it. This means we need a constant supply through our diet to ensure enough Zinc for our body's needs. Hence, understanding Zinc and its vital role in our health is crucial to ensuring we're getting the right amount for optimal wellbeing.
Zinc holds a significant position as the second-most abundant trace mineral in your body, following iron. It is present in every cell, facilitating the functioning of over 300 enzymes responsible for metabolism, digestion, nerve function, and other vital processes.
Moreover, Zinc plays a pivotal role in the development and functionality of immune cells. It is essential for maintaining skin health, facilitating DNA synthesis, and promoting protein production. The growth and division of cells are also dependent on serum zinc levels. Additionally, Zinc contributes to your senses of taste and smell by supporting the enzyme crucial for these sensory perceptions.
So, now that we've understood what Zinc is let's explore its various roles in more detail.

Immune Function
Did you know Zinc is one of the key warriors in your immune system's defence line? When you catch a common cold, however, one of the first suggestions is often to take Zinc. This is because it works relentlessly to fight off invading bacteria and viruses.
It's no exaggeration to say that Zinc is a mighty soldier standing guard over your immune system. But how does it work? Let's delve deeper into Zinc's role in your immune function.
Zinc is a critical component when fighting off intruders like bacteria and viruses. It's involved in every stage of the immune response. Zinc helps maintain the integrity of your skin and mucous membranes—the body's first defence against pathogens. It also supports the function of your white blood cells, including T, B, and natural killer cells. These cells identify, target, and kill invading organisms, and Zinc plays a part in their production and activation.

One area where Zinc's role has been heavily researched is reducing the duration and severity of the common cold. It turns out that this humble mineral, Zinc, may interfere with viruses' process to latch onto our cells. When taken at the first sign of a common cold, Zinc can help block this process, helping to stop the common cold in its tracks or at least lessen its severity and duration.
Furthermore, Zinc has antioxidant properties, meaning it fights off free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause damage to our cells. This adds another layer to its immune-boosting capabilities, as keeping our cells healthy is crucial for a robust immune response.
But remember, while Zinc plays a crucial role in our immune function, it's only one piece of the puzzle. A healthy lifestyle, balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management contribute to a well-functioning immune system.
Understanding the role of Zinc in our immune function underlines the importance of ensuring we're getting enough of this powerful mineral in our diet. Now that's something to remember next time you reach for your vitamin and mineral supplements at the first signs of a sniffle!

Metabolism
Zinc is the unsung hero of our body's metabolic function. It helps synthesise proteins, aids in wound healing and is involved in DNA synthesis and cell division.
Our bodies are like complex machines with several processes running simultaneously to keep us alive and thriving. One of these processes is metabolism - and guess what? Zinc is deeply involved here, too!
Zinc's role in metabolism is multi-faceted. It's involved in the structure and function of many proteins and enzymes in our body, playing a pivotal role in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It helps convert our food into energy, helping us stay active and alert.
Additionally, zinc aids in the process of cellular metabolism. It supports the function of around 300 enzymes that aid in metabolism, digestion, nerve function, and many other processes. It also plays a role in the production, storage and secretion of insulin, a key hormone in glucose metabolism.
The importance of Zinc in metabolism cannot be overstated. Without it, the processes that keep us running could falter.

Skin Health
Zinc doesn't just work on the inside - it's crucial for our outside as well, specifically for our skin. It's known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce redness and inflammation associated with acne and pimples.
Furthermore, due to its role in cell growth and replication, zinc oxide helps your skin heal and rejuvenate, contributing to a healthy complexion. It's involved in the breakdown of collagen, which aids in wound healing and regenerating new skin cells.
Some research also suggests that zinc oxide may act as a natural sunblock, offering protection against harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, although it's not a replacement for a good sunblock cream.

Sense of Taste and Smell
One of the more fascinating roles of Zinc is its involvement in our sense of taste and smell. It's necessary for the proper development and function of cells that make up the olfactory system, which is responsible for our sense of smell. Similarly, Zinc also supports the gustatory system, affecting our ability to taste.
Studies have shown that zinc deficiencies can lead to an impaired sense of taste and smell, emphasizing the importance of adequate zinc levels in our diet.
With so many roles in our body, from supporting our immune function, aiding metabolism, and promoting skin health to enhancing our senses, it's clear that Zinc is not just a trace mineral in our diet but a trace mineral that traces its way to almost every aspect of our health!
In the next section, let's find out where we can get this essential nutrient from and how to recognize if we're falling short.
Unveiling the Health Benefits of Zinc Vitamin
Research reveals a multitude of health benefits associated with zinc consumption.
1. Boosts Your Immune System
Zinc plays a vital role in fortifying your immune system. Its involvement in immune cell function and cell signalling ensures a robust immune response. Zinc deficiency can lead to a weakened immune system. Zinc supplements stimulate specific immune cells and mitigate oxidative stress. Several studies demonstrate that zinc intake of 80–92 milligrams (mg) per day can reduce the duration of the common cold by up to 33%. Older adults who take zinc supplements experience improved immune response and reduced risk of infections.
2. Accelerates Wound Healing
The medical community widely employs Zinc in treating burns, certain ulcers, and other skin injuries. This is because Zinc is instrumental in collagen synthesis, immune function, and the inflammatory response, which are crucial for wound healing. Your skin holds a relatively high amount of Zinc, approximately 5% of your body's zinc content. While a zinc deficiency can impede wound healing, supplementation with Zinc can expedite recovery. Studies show that individuals with diabetic foot ulcers treated with 50 mg of zinc per day experience significant reductions in ulcer size compared to those in the placebo group.
3. Reduces the Risk of Age-Related Diseases
Zinc intake may significantly decrease the likelihood of age-related diseases such as pneumonia, infection, and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Zinc helps relieve oxidative stress and enhances immune response by boosting the activity of T-cells and natural killer cells, safeguarding your body from infections. Older adults who supplement with elemental Zinc may demonstrate improved influenza vaccination response, a decreased risk of pneumonia, and enhanced mental performance. Research suggests that 45 mg per day of elemental Zinc can decrease the incidence of infection in older adults by nearly 66%. Furthermore, a study involving over 4,200 participants found that daily antioxidant supplements, combined with 80 mg of elemental Zinc, reduce vision loss and significantly lower the risk of advanced AMD.
4. May Help Treat Acne
Acne, a prevalent skin condition affecting approximately 9.4% of the global population, can be effectively addressed with zinc treatments. Both topical and oral zinc treatments exhibit efficacy in reducing inflammation, inhibiting the growth of P. acnes bacteria, and suppressing oil gland activity. Studies have shown that individuals with acne often have lower zinc levels, making zinc supplementation more beneficial in reducing symptoms and promoting clearer skin.

5. Decreases Inflammation
Zinc significantly reduces oxidative stress and lowers levels of certain inflammatory proteins in the body. Chronic inflammation contributes to various chronic illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and mental decline. By decreasing oxidative stress, Zinc helps mitigate chronic inflammation, promoting overall health and wellbeing. In a study involving older adults, those taking 45 mg of Zinc daily experienced greater reductions in inflammatory markers compared to the placebo group.
Deficiency Symptoms and Risk Factors
While severe zinc deficiency is rare, milder forms are more common, especially in children in developing countries with inadequate diets. Symptoms of mild zinc deficiency include diarrhoea, decreased immunity, thinning hair, poor taste or smell, dry skin, fertility issues, and impaired wound healing. Certain individuals are at a higher risk of zinc deficiency, including those with gastrointestinal diseases like Crohn's disease, vegetarians and vegans, pregnant or breastfeeding women, older infants who are exclusively breastfed, individuals with sickle cell anaemia, malnourished individuals, those with chronic kidney disease, and those with alcohol use disorder.

Natural Sources of Zinc
Now that we've recognised its importance, where can we get Zinc? Plenty of animal products, such as meat, shellfish, and dairy, are rich in Zinc.
Conversely, plant-based foods like whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds also offer Zinc, albeit in a less bioavailable form.
It's clear that Zinc is vital for our health, but where can we find it? Thankfully, Zinc is available in a variety of both animal-based and plant-based foods.
Animal products are excellent sources of high doses of Zinc too. Red meat, such as beef, lamb, and pork, is rich in Zinc. Poultry and seafood, especially oysters, crab, and lobster, also contain substantial amounts of this essential mineral. Additionally, dairy products like cheese and milk offer a good source of Zinc.

For the vegetarians and vegans out there, fear not! There are plenty of plant-based foods that can help meet your zinc needs. Whole grains, legumes (like chickpeas, lentils, and beans), nuts, and seeds provide Zinc. Foods like tofu, tempeh, and fortified breakfast cereals can also increase your intake of elemental zinc.
However, it's important to note that Zinc from plant-based sources isn't as easily absorbed by the body as from animal products. This is due to phytates—a plant compound that inhibits zinc absorption. However, certain food preparation methods, like soaking and sprouting grains, nuts, and legumes, can help reduce phytate levels and improve zinc absorption.
Zinc Deficiency
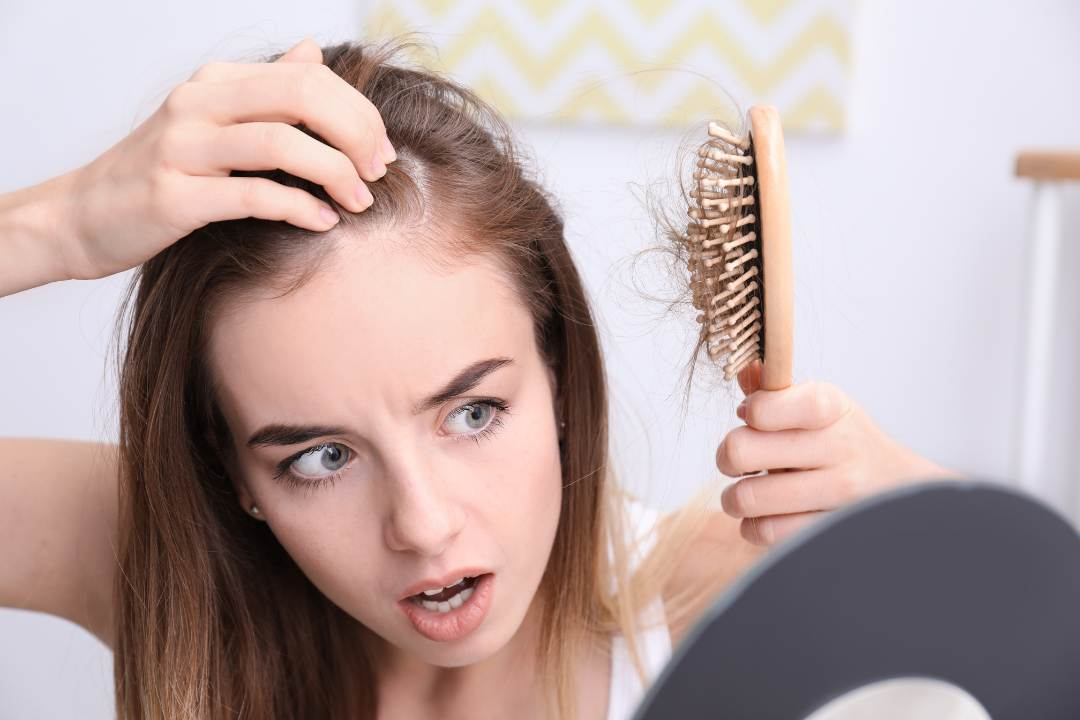
Recognising the signs and symptoms of zinc deficiency is crucial. Symptoms of copper deficiency can vary from hair loss, skin rashes, and loss of appetite to a weakened immune function.
While it's relatively rare in developed countries, zinc deficiency can occur and can lead to various signs and symptoms. These may include loss of appetite, slowed growth, weight loss, delayed sexual maturation, impotence, hair loss, eye and skin lesions, and impaired immunity.
People with digestive disorders, vegetarians, pregnant and lactating women, and sickle cell disease are more at risk of zinc deficiency. If you think you may be deficient in Zinc, seeking advice from a healthcare provider is important.

Risks of Excessive Zinc
While Zinc is essential for our health, too much can be harmful. Consuming excessive doses of Zinc can lead to toxicity and interfere with absorbing other essential minerals like copper and iron. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach cramps, diarrhoea, and headaches.
It's crucial to remember that while dietary supplements can help us meet our nutritional needs, getting nutrients from a balanced diet should always be the first defence. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new dietary supplement regimen.
The Importance of Balanced Zinc Intake
This leads us to the importance of balance. A copper deficiency and excess or low zinc levels may lead to health issues, underscoring the need for a balanced zinc intake.
Even with Zinc, balance is key as with all things in life. Too much Zinc or little can lead to deficiencies, while too much Zinc can lead to toxicity. Maintaining a balanced zinc intake is vital for overall health and wellbeing.
In the next section, we'll delve into the effects of zinc supplements, exploring who might benefit from them and how they can help bridge the nutritional gap.
Zinc Supplements
In a perfect world, we get all the nutrients we need from our diet alone. However, it may be necessary to consider supplements due to dietary restrictions, health conditions, or a lack of access to nutrient-rich foods. Zinc supplements can play a crucial role in helping to meet our nutritional needs.
Zinc supplements come in various forms, including zinc gluconate, zinc gluconate sulfate, and even Zinc gluconate acetate. They all serve the primary purpose of boosting your zinc levels, but their bioavailability can differ.
Supplements can be particularly useful for certain groups. For instance, vegetarians and vegans, who might struggle to get enough Zinc from their diet due to their lower bioavailability in plant-based foods, could benefit from a zinc supplement.

Similarly, individuals with certain health conditions that affect nutrient absorption, such as Crohn's disease or celiac disease, might also find taking high doses of Zinc in supplements beneficial. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, who need higher amounts of Zinc, might also require supplementation under the advice of a healthcare provider.
While zinc supplements can be useful, using them responsibly is crucial. They're not meant to replace a balanced, healthy diet of zinc intake but rather to complement it. It's also important to remember that excessive zinc intake can lead to toxicity. Therefore, always consult a healthcare provider before starting a zinc supplement regimen.
Terranova Zinc 15 mg Complex: This supplement comprises Zinc as bisglycinate chelate (TRAACS™), a highly bioavailable form of Zinc. This form of Zinc allows for optimal absorption. It plays multiple roles in immune function, reproductive health, wound healing, skin health, and more, making it a crucial nutrient for maintaining good health.
Viridian Balanced Zinc Complex: The product supports immunity and cognitive functions, as well as helps to keep bones, eyes, skin, hair, and nails in good condition. It also contributes to normal fertility and reproductive health in men and women.
Willow Zinc/Magnesium/B6: This is a natural mineral supplement of zinc gluconate, magnesium aspartate, and vitamin B6. Zinc supports the immune system and muscles. Magnesium plays a role in metabolism and muscle health and helps manage sleep. Vitamin B6 may boost energy, maintain healthy blood vessels, support brain function, and improve mood. Each capsule contains a 590mg proprietary blend of magnesium glycinate, zinc gluconate, and pyridoxine (B6).
Mineralife Zinc: This supplement is an advanced aqueous form of zinc ions (IsoIonic™) in a clear solution, allowing quicker absorption than tablets or capsules. It supports healthy immune function, mental health, libido, red blood cell levels, fertility, memory function, blood glucose levels, oral and teeth health, cardiovascular health, eating patterns, urinary tract, weight management, hair and skin, the pressure within blood vessels, eye tissue, and intestinal and digestive tract. The product also includes CHD-Fulvic Acid to enhance absorption and overall wellbeing.
GOODHEALTH Zinc Melts: These zinc supplements are designed to melt in your mouth for quick absorption. They provide the daily recommended dose of Zinc, a crucial mineral for immune support, wound healing, and maintaining a sense of taste and smell.
SFERA Zinc Complex: This complex supplement combines Zinc with complementary vitamins and minerals, optimizing absorption and promoting overall health. It supports the immune system, hormone regulation, and skin health.
WILLOW Zinc: WILLOW Zinc provides pure Zinc for targeted zinc supplementation. It supports immune function, protein synthesis, and metabolic function.
WILLOW Vitamin A to Zinc: A comprehensive multivitamin supplement covering essential vitamins from A to Zinc, promoting overall health and wellness.
YOUR WELLBEING Zinc Glycinate Plus: Featuring Zinc in the highly absorbable glycinate form, this supplement also includes additional nutrients for synergistic benefits.
GOODHEALTH Viralex Attack: This rapid-response immune support supplement with key ingredients like Zinc, olive leaf, and astragalus.
ZINPLEX Forte: An enhanced zinc formula designed for individuals with greater zinc needs, often recommended for skin health, immunity, and testosterone balance.
ZINPLEX: A standard zinc supplement to support immune function, digestion, and overall wellness.
GOODHEALTH Viralex: A daily immune support supplement with standardized ingredients such as olive leaf extract, Zinc, and selenium.
WILLOW Virimale: A men's health supplement that combines Zinc with other key nutrients to support vitality, immune function, and reproductive health.
VIRIDIAN High Five Multivit & Mineral Complex: A high-quality multivitamin and mineral supplement providing a range of essential nutrients, including Zinc, for general health support.
GOODHEALTH Women's Multi: A multivitamin tailored for women's unique nutritional needs, including adequate Zinc levels for immune support and hormone balance.
GOODHEALTH Vitamin C Plus: A vitamin C supplement with additional Zinc for synergistic immune support.
ZINPLEX Triple: An intensified zinc formula offering triple the amount of Zinc for targeted nutritional support.
TERRA NOVA Prenatal Multivitamin Complex: A comprehensive prenatal dietary supplement provides expectant mothers with essential vitamins and minerals, including Zinc.
GOODHEALTH Viralex Kids: An immune support supplement for children, combining Zinc with other child-friendly vitamins and minerals.
METAGENICS Phytomulti Tabs: A premium multivitamin supplement featuring a blend of plant-based nutrients and essential vitamins and minerals.
METAGENICS Phytomulti With Iron Tabs: Similar to the previous supplement, but with added iron to support blood health.
WILLOW Flugo: An immune support supplement which combines various vitamins, minerals, and plant extracts to maintain health during flu season.
METAGENICS PhytoMulti Capsules: The capsule version of the METAGENICS Phytomulti provides phytonutrients, vitamins, and minerals for comprehensive support.
METAGENICS Zinc Drink: A drinkable zinc supplement for rapid absorption and immediate immune support.
METAGENICS Zinc AG: Featuring a unique patented process that enhances the absorption rate of zinc oxide, aiming to provide rapid and efficient immune support.

Who Should Take Zinc Supplements?
Certain groups may benefit more from dietary supplements, including vegetarians or those with certain digestive disorders. However, it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider first.
As stated earlier, certain people may benefit more from taking zinc supplements alone. This includes individuals with certain dietary restrictions, like vegetarians and vegans, and those with specific health conditions affecting nutrient absorption. However, zinc supplementation should always be under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
We've covered a lot of ground on our journey through the Zinc world. From understanding what it is to its various roles in the body, to the foods that contain it, signs and effects of zinc deficiency, and even supplements. But before we wrap up, let's take a moment to answer some frequently asked questions about Zinc.
In essence, the importance of Zinc cannot be overstated. From supporting our immune system and metabolism to promoting skin health and our sense of taste and smell, this essential mineral is a powerhouse. A balanced diet that includes more zinc-rich foods can help maintain optimal health. However, in some cases, supplementation of excess Zinc might be necessary. The goal should always be maintaining a balanced zinc intake to reap its numerous health benefits.

Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and the Role of Zinc
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. Zinc has been studied for its potential role in preventing and treating AMD. Research suggests that Zinc may help reduce the risk of developing advanced AMD and slow its progression.
Zinc Sulphate: A Common Form of Supplemental Zinc
Zinc sulphate is a common zinc supplement used to address zinc deficiencies. The body easily absorbs it, which can be found in various over-the-counter zinc supplements. Zinc sulphate supplementation is often recommended for individuals with low zinc levels, as it helps restore zinc status and supports overall health.
Supplemental Zinc: Benefits and Considerations
Supplemental Zinc is widely available and used for various health purposes. It offers several benefits, including supporting immune function, promoting wound healing, aiding DNA synthesis, and supporting proper growth and development. However, it's essential to consider proper zinc dosage and consult a healthcare professional before starting zinc supplementation to ensure safety and avoid potential side effects.

Low Levels of Zinc: Symptoms and Consequences
Low levels of Zinc, also known as zinc deficiency, can lead to a range of symptoms and health consequences. Common symptoms include impaired immune function, decreased appetite, hair loss, delayed wound healing, and changes in taste and smell. Prolonged zinc deficiency can have more severe consequences, such as growth retardation, sexual maturation delay, and increased susceptibility to infections. It is crucial to address the effects of zinc deficiency through dietary changes and, if necessary, zinc supplementation.
Zinc Citrate: An Alternative Form of Zinc Supplement
Zinc citrate is another zinc sulfate supplement commonly used to address some zinc sulfate deficiencies. It is well-absorbed by the body and often found in various dietary supplements. Zinc citrate offers similar benefits as other supplemental forms with zinc sulfate and can be a suitable option for individuals seeking an alternative to zinc sulphate.

Zinc Status: Assessing Zinc Levels in the Body
Assessing zinc status is important to determine if an individual has adequate or deficient serum zinc levels. Blood tests can measure zinc levels but may not always accurately reflect the body's serum zinc amount status since serum zinc amount is tightly regulated. Other factors, such as dietary zinc intake and genetics, should be considered alongside blood results to determine zinc status and the need for supplementation.
Oral Zinc: Administration and Absorption
Oral zinc supplements are commonly used for addressing zinc deficiencies. They are available in various forms, including tablets and capsuleZincnd liquid formulations. When taken orally, zinc is absorbed in the small intestine. However, factors such as other dietary components, medications, and individual variations in absorption capacity can influence zinc absorption.
Zinc plays a significant role in various aspects of health, including age-related macular degeneration, zinc supplementation reduces and for zinc deficiency, and maintaining optimal zinc status. Zinc sulphate and zinc citrate are Zinconly-used forms of supplemental zinc, and assessing zinc levels through blood tests is essential. Oral zinc supplements are widely available, but proper administration and absorption considerations should be considered for optimal effectiveness. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized guidance regarding zinc treatment and supplementatiZincon.

FAQ
Q1: How much more zinc should I take daily?
A1: The recommended daily amount of zinc for adult men is 11mg and 8mg for women. However, the required zinc intake can vary based on individual needs, age, and overall health.
Q2: Can taking zinc cold symptoms or combating common colds?
A2: Some studies suggest that zinc can reduce the duration and severity of the common first cold symptoms, particularly zinc treatment, within 24 hours of ingesting zinc.
Q3: Can taking too much zinc be harmful?
A3: Excessive effects of zinc can interfere with the absorption of other minerals like zinc may copper and can cause nausea, vomiting, and weakened immunity.
Q4: Are there any natural food sources rich in copper deficiency zinc?
A4: Yes, oysters, red meat, peas, lentils, poultry, beans, nuts, and dairy products are rich in zinc.
Q5: Can vegetarians meet their zinc needs without taking zinc supplements?
A5: Yes, vegetarians can meet their zinc daily allowance by eating plant-based sources like beans, legumes, nuts, and whole grains. However, zinc from plant sources is less bioavailable, so they might need to consume more of these foods to meet their requirements.
